Java JOptionPane
JOptionPane 使用整理
Import 起手式
1 | import javax.swing.JOptionPane; |
Kind
- showConfirmDialog(): Asks a confirming question, like yes/no/cancel.
1
showConfirmDialog();
- showInputDialog(): Prompt for some input.
1
showInputDialog();
- showMessageDialog(): Tell the user about something that has happened.
1 | showMessageDialog(); |
- showOptionDialog(): The Grand Unification of the above three.
1
2
3JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(parentComponent, Object Message, String title, int optionType, int messageType, Icon icon, Object[] options, Object initialValue);
//JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(父元素元件, 顯示的訊息, 顯示的訊息標題, 顯示選項類型, 顯示的訊息類型, 圖示, 按鈕的選項, 預設按鈕);showOptionDialog() E.g.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
import javax.swing.*;
public class ConfirmDialog1a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
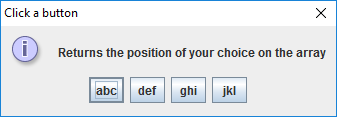
String[] options = {"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl"};
//Integer[] options = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11};
//Double[] options = {3.141, 1.618};
//Character[] options = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'};
int x = JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null, "Returns the position of your choice on the array",
"Click a button",
JOptionPane.DEFAULT_OPTION, JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE, null, options, options[0]);
System.out.println(x);
}
}
Parameters
parentComponent
Defines the Component that is to be the parent of this dialog box. It is used in two ways: the Frame that contains it is used as the Frame parent for the dialog box, and its screen coordinates are used in the placement of the dialog box. In general, the dialog box is placed just below the component. This parameter may be null, in which case a default Frame is used as the parent, and the dialog will be centered on the screen (depending on the L&F).
message
A descriptive message to be placed in the dialog box. In the most common usage, message is just a String or String constant. However, the type of this parameter is actually Object. Its interpretation depends on its type:
- Object[]: An array of objects is interpreted as a series of messages (one per object) arranged in a vertical stack. The interpretation is recursive – each object in the array is interpreted according to its type.
- Component: The
Componentis displayed in the dialog. - Icon: The
Iconis wrapped in aJLabeland displayed in the dialog. - others: he object is converted to a
Stringby calling itstoStringmethod. The result is wrapped in aJLabeland displayed.
messageType
Defines the style of the message. The Look and Feel manager may lay out the dialog differently depending on this value, and will often provide a default icon. The possible values are:
-
ERROR_MESSAGE -
INFORMATION_MESSAGE -
WARNING_MESSAGE -
QUESTION_MESSAGE -
PLAIN_MESSAGE
optionType
Defines the set of option buttons that appear at the bottom of the dialog box:
-
DEFAULT_OPTION -
YES_NO_OPTION -
YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION -
OK_CANCEL_OPTION
You aren’t limited to this set of option buttons. You can provide any buttons you want using the options parameter.
options
A more detailed description of the set of option buttons that will appear at the bottom of the dialog box. The usual value for the options parameter is an array of Strings. But the parameter type is an array of Objects. A button is created for each object depending on its type:
- Component: The component is added to the button row directly.
- Icon: A
JButtonis created with this as its label. - other: The
Objectis converted to a string using itstoStringmethod and the result is used to label aJButton.icon
A decorative icon to be placed in the dialog box. A default value for this is determined by themessageTypeparameter.title
The title for the dialog box.
initialValue
The default selection (input value).